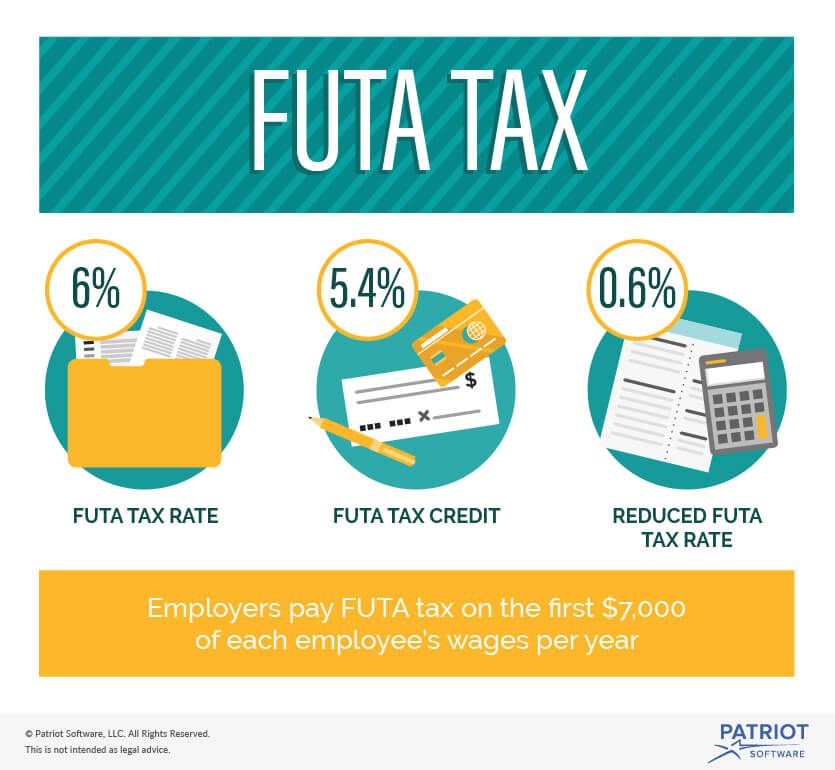
State unemployment tax act (suta) indiana code 22 article 4. The futa tax is 6 percent of an employee’s first $7,000 of gross pay, but employers are entitled to a substantial rate deduction if the state they operate in complies with futa guidelines.

What Is Unemployment Tax And How Much Are You Going To Pay - Workest
This tax is similar to the futa tax that the federal government levies on employers.
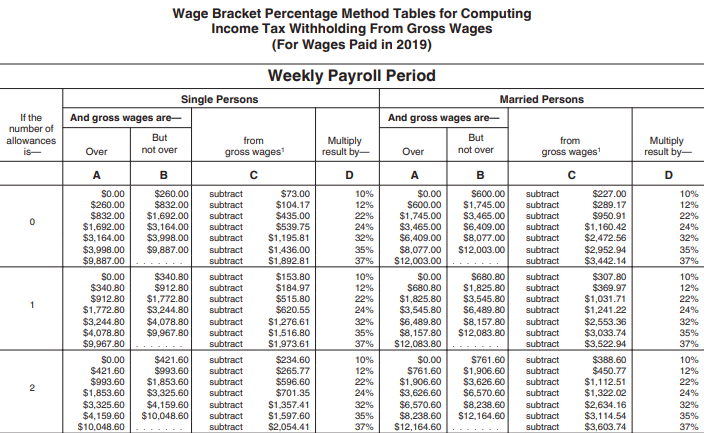
What is suta tax on my paycheck. 52 rows this means you will only contribute unemployment tax until the. These contributions provide monetary support to displaced workers. Just as futa taxes fund federal unemployment programs, suta taxes fund your state’s unemployment insurance program.
Who has to pay futa and suta taxes? What is the suta tax? State unemployment tax assessment (suta) is based on a percentage of the taxable wages an employer pays.
If one of your employees ever gets laid off and starts collecting state unemployment insurance, it’s likely that money will come from your state’s state unemployment tax act fund. The futa and suta taxes are filed on form 940 each year, regardless if a business has an employee on unemployment. Suta, or the the state unemployment tax act (suta), is a payroll tax paid by all employers at the state level.
The state unemployment tax act (suta) tax is a type of payroll tax that states require employers to pay. What does suta tax mean? The futa tax rate is 6% and applies to the first $7,000 paid to each employee as wages during the year.
The $7,000 is often referred to as the federal or futa wage base. Besides the fica tax, there are different types of related taxes called futa and suta which are simply unemployment taxes. The suta tax is the state version of the futa tax.
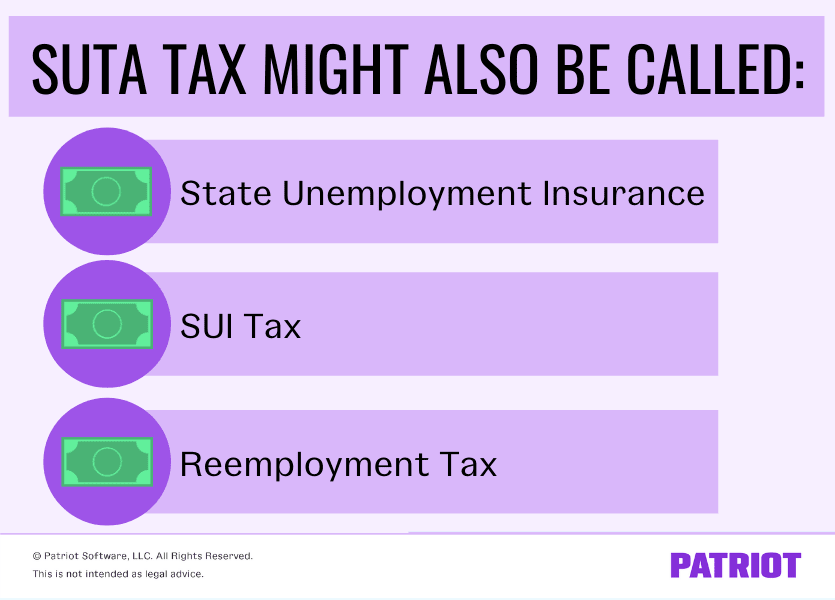
The state unemployment tax act (suta) requires employers to pay a type of payroll tax. The percentage of the suta tax varies from state to state. States may also refer to suta tax as state unemployment insurance, sui, or reemployment tax in florida.
It’s important to calculate suta taxes in conjunction with the futa tax. However, it is always a simple percentage of the employee’s pay up to a yearly earnings limit. The state unemployment tax act, also called suta, imposes a tax on the wages that employers pay to their employees.
The state unemployment tax act, known as suta, is a payroll tax employers are required to pay on behalf of their employees to their state unemployment fund. States might also refer to suta tax as the following: The $7,000 is often referred to as the federal or futa wage base.
Some states use the same wage base as the federal wage base (of $7,000), others do not. State unemployment tax act (suta): These contributions provide monetary support to displaced workers.
Equal opportunity is the law. This tax is used by the state to fund the unemployment insurance programs to benefit fired or laid off employees. Employers are required to pay both state unemployment payroll taxes (suta) and federal unemployment payroll taxes (futa).
Like other payroll taxes, you pay suta taxes on a percentage of each employee’s earnings, up to a certain amount. This provides benefits in the form of money to people who have lost their jobs (there are additional requirements to collect sui, including that you have lost the job through no fault of your own. This is a payroll tax collected by your state to fund unemployment insurance benefits to workers.
Over the course of the quarter, if their total payments totaled $22,500, the amount to be deposited to the sui fund would total $13.50 ($22,500 x 0.0006 = $13.50). States use funds to pay out unemployment insurance benefits to unemployed workers. This entitles you to receive a monthly social security payment upon retirement.
What is the state unemployment tax (suta)? The state unemployment tax act is a tax that states use to fund unemployment benefits. Suta was established to provide unemployment benefits to displaced workers.
Thus, an individual with wages equal to or larger than $ 128,400 would contribute $ 7,960.80 to the oasdi program in 2018, as would his or her employer. For wages paid in 2018, employees and employers pay 6.2 percent in oasdi taxes. Accordingly, what is the suta rate for 2019?
The money collected through suta tax funds the state unemployment insurance to employees who lost their job through no fault of their own. It is the employer's responsibility to withhold the tax and make payments. Employers pay state unemployment insurance contributions based on what they pay their employees, up to a certain state wage base.
Some states require that both the employer and employee pay suta taxes. Taxes under state unemployment tax act (suta) are those designed to finance the cost of state unemployment insurance benefits in the united states, which make up all of unemployment insurance expenditures in normal times, and the majority of unemployment insurance expenditures during downturns, with the remainder paid in part by the federal. Suta was developed in each state alongside the federal unemployment tax.
The state unemployment tax act, known as suta, is a payroll tax employers are required to pay on behalf of their employees to their state unemployment fund. Suta, the state unemployment tax act, is the state unemployment insurance program to benefit workers who lost their jobs. As with almost all state regulations, the rules that company owners must follow for suta vary by state.
Employers contribute to the state unemployment program by paying suta tax every quarter, depending on the suta tax rate and the wage base. ( la igualdad de oportunidad es la ley.) equal opportunity employer/program auxiliary aids and services are available upon request to. Some states apply various formulas to determine the taxable wage base, others use a percentage of the state’s average annual wage, and many simply follow the futa wage base.
Employers pay suta tax, also known as state unemployment insurance (sui) tax, based on their employees' wages. The suta program was developed in each state in 1939 during the great depression, when the u.s. The state unemployment tax, also called the state payroll tax or simply ‘ suta ,’ is a payroll tax you pay into your state’s unemployment benefits fund.
State unemployment insurance (sui) :

What Is Futa Paychex
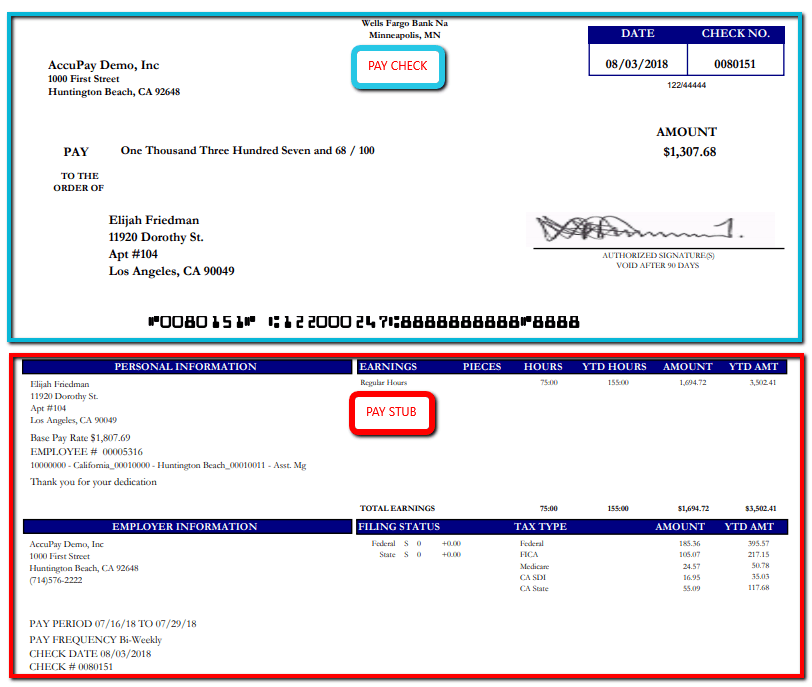
A Guide On How To Read Your Pay Stub - Accupay Systems
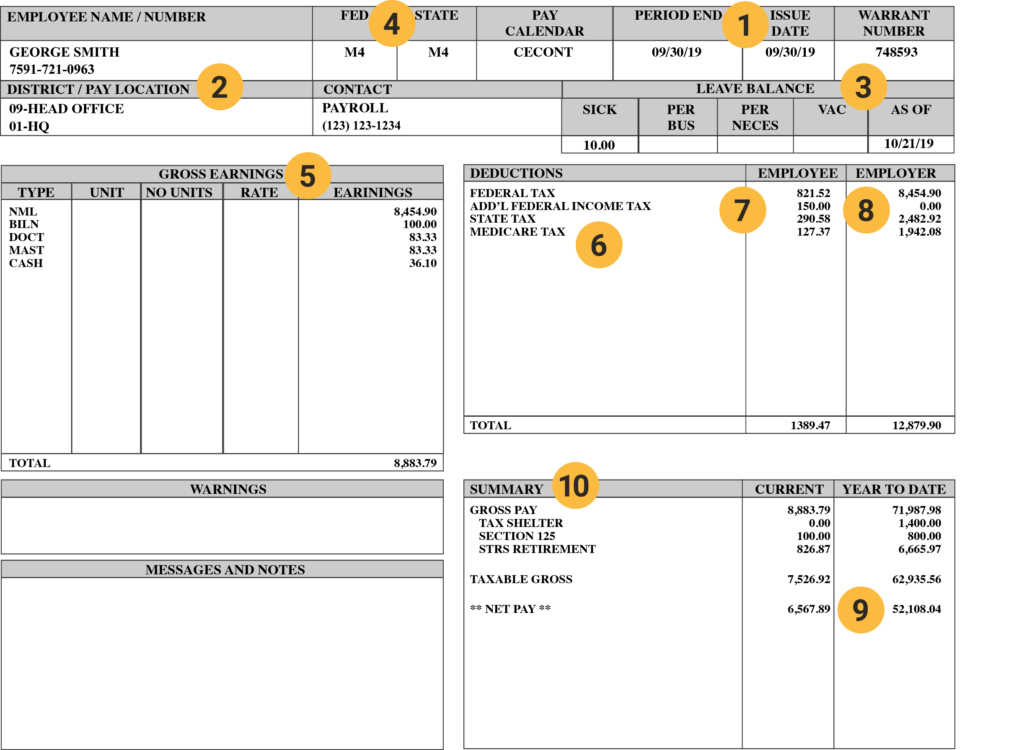
Understanding Your Paycheck Stub Information Earnings Deductions How To Read Your Pay Stub Iris Fmp
Are Employers Responsible For Paying Unemployment Taxes
Setting Up Suta In Payroll
What Is Suta Tax Definition Rates Example More
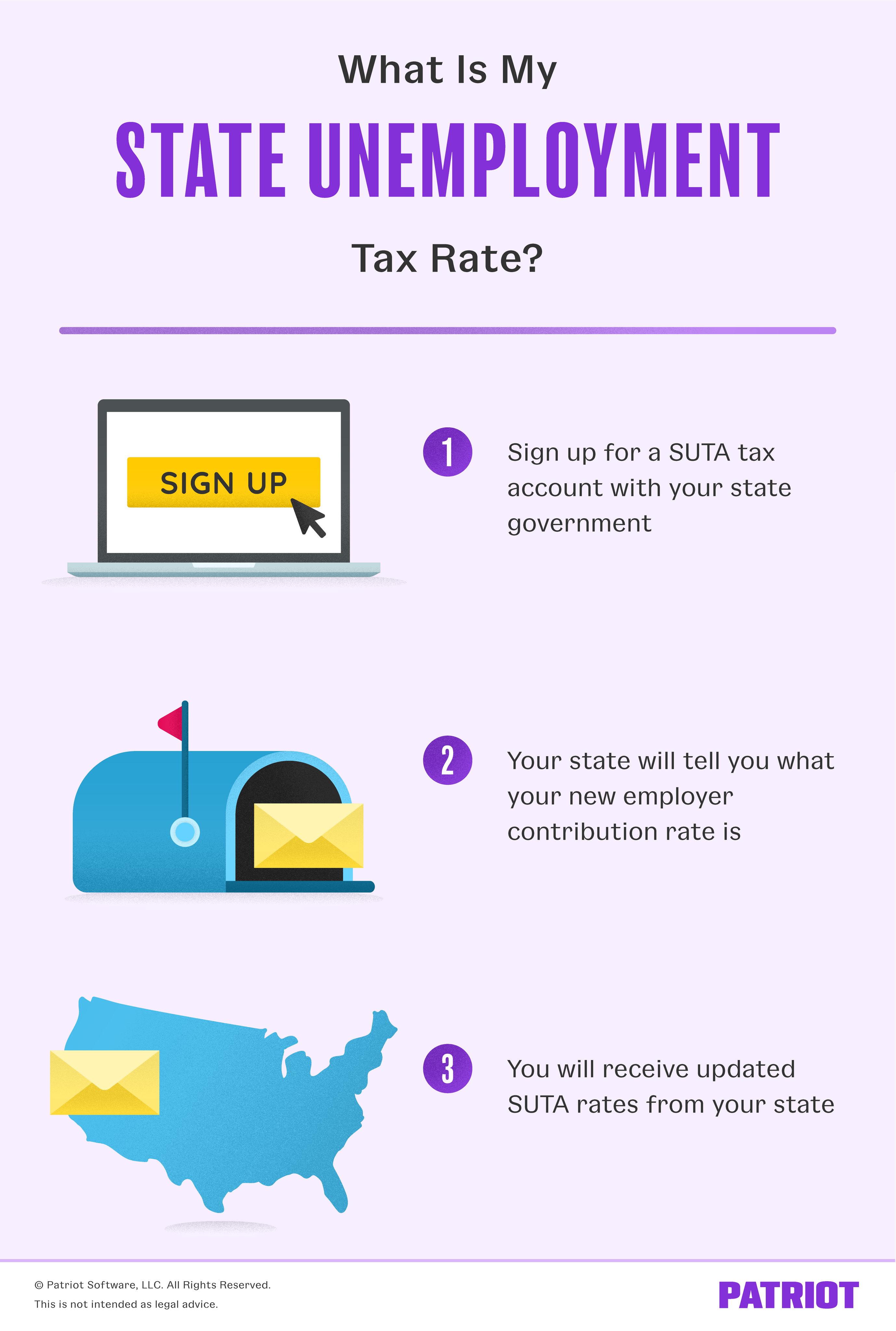
What Is My State Unemployment Tax Rate 2021 Suta Rates By State

Tax Information Career Training Usa Interexchange

Understanding Your Paycheck Creditcom
Payroll Taxes Explained - Cashay
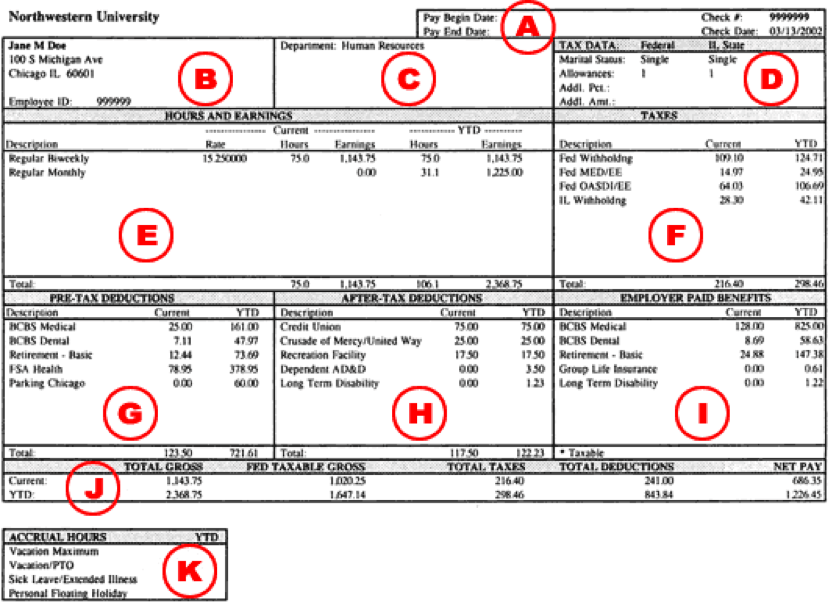
Understanding Your Paycheck Human Resources - Northwestern University
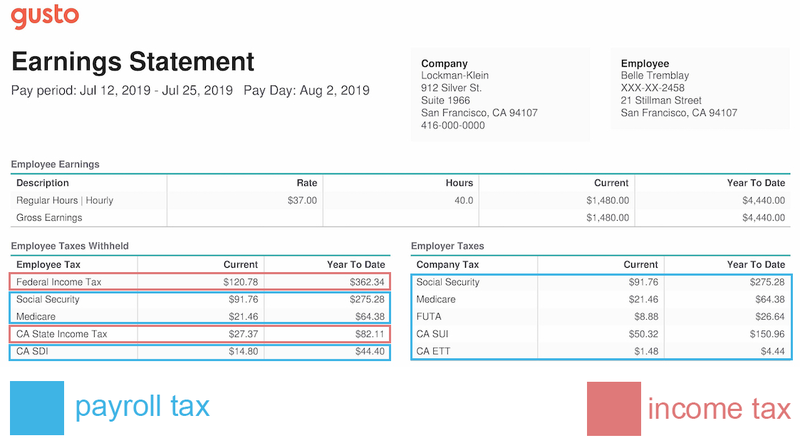
Payroll Tax Vs Income Tax Whats The Difference The Blueprint

How To Explain Paycheck Withholdings Deductions Contributions To Your Employees Score

Payroll Taxes Explained - Cashay

What If Quickbooks Payroll Taxes Are Not Computing - Insightfulaccountantcom

How Do I Read My Pay Stub Gusto
/payroll-taxes-3193126-FINAL-ef94c8b30eda48fdbde6ab58d9a30d49.png)
Payroll Taxes And Employer Responsibilities

Payroll Tax What It Is How To Calculate It Bench Accounting
/when-you-can-expect-to-get-your-first-and-last-paycheck-2060057_FINAL-5c6c1bc446e0fb000165cba9.png)
When You Can Expect To Get Your First And Last Paycheck

Comments
Post a Comment